Urban circular economy as a future model: efficiency, sustainability and digital transformation in cities
Circular economy for districts, cities, and municipalities aims to use resources efficiently, minimize waste, and close material cycles in urban areas. Through the principles of reduce, reuse, and recycle, strategies can be developed that support the circularity of cities across various domains. By reusing, recycling, and recovering materials, cities can reduce their dependence on finite resources and promote sustainable economic models.
However, key challenges lie in the implementation of suitable infrastructures, the creation of economic incentives, the legal framework such as statutory warranties, and the integration of circular economy principles into existing urban planning and supply systems. In addition, urban circular economy requires new cooperation models between municipalities, cities, businesses, and citizens, as well as the use of digital technologies to manage and optimize material flows.
Sustainable Digitalisation: urban circular economy & saving resources
We support the transformation through the digitalisation of processes that enable a holistic perspective while creating transparency. Our concepts for urban circular economy include
- the sustainable design of energy and resource use,
- mobility solutions with sharing concepts, as well as
- awareness-raising for active forms of mobility.
Another focus is on the urban circularity of real estate projects, for example through urban mining, to promote the reuse of building materials and the minimisation of waste.
AIT services for the circular economy in districts, cities and municipalities
AIT supports you with the following topics:
- Urban resource flows – analysis and synthesis of urban mining strategies
- Circular economy strategies at the district level
- Multifunctional use of space to conserve resources
Urban resource flows – analysis and synthesis of urban mining strategies
We support cities and urban stakeholders in the analysis and strategic implementation of circular economy concepts by applying scientific methods for capturing and modeling urban material flows. Through the development of scenarios and the evaluation of circular strategies, we enable data-driven decision-making processes that promote sustainable resource use.
Our research approaches include the development of tools for urban administrations that facilitate the practical implementation of circular economy principles. Advising cities and districts on long-term strategies is also a key component of our service portfolio.
In addition, we support participatory co-creation in planning processes to develop application-oriented solutions for resilient and resource-efficient urban development strategies.
Circular economy for districts, cities and municipalities: strategies for districts
In a holistic approach to sustainable district development, the topic of decarbonisation holds great importance. We address circular economy through lifecycle analyses of buildings, evaluation of the CO2-binding potential of vegetation, as well as sustainable procurement and deconstruction concepts.
By evaluating the framework conditions for districts (both existing and new developments), comprehensive strategies can be derived and developed to achieve a climate-neutral district. We analyze embodied CO2 in buildings as well as operational CO2 (for example, emissions from energy and mobility) in order to derive effective measures.
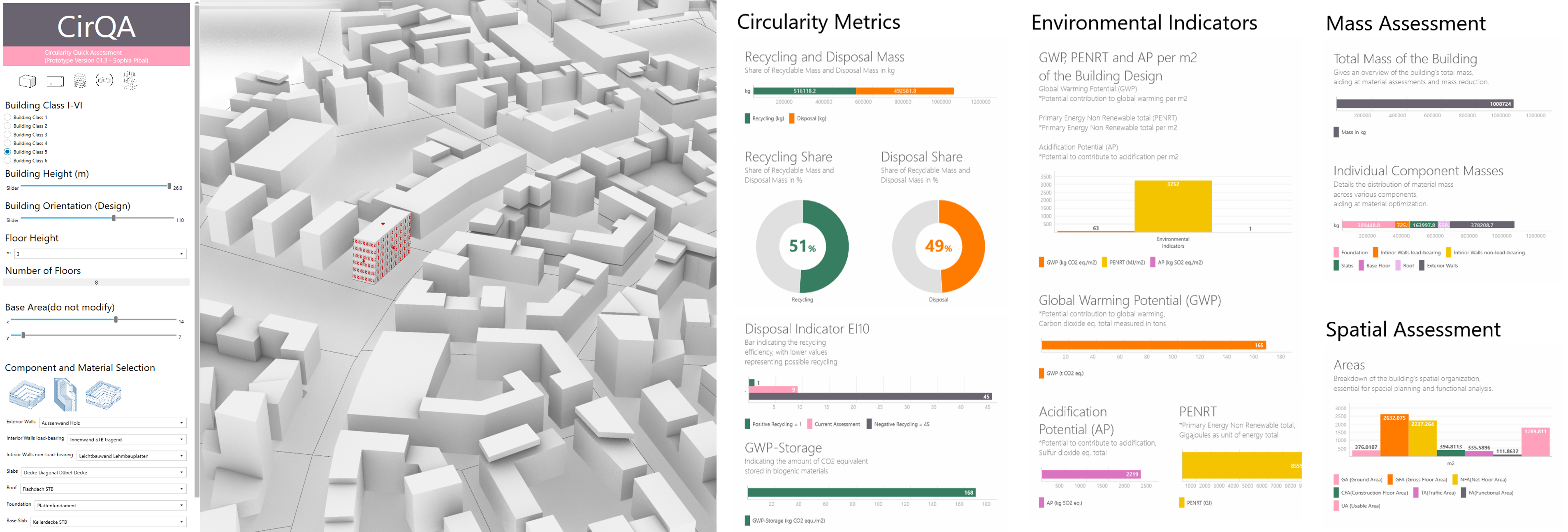
CirQA tool for rapid assessment of circularity in the early stages of building design
Circular economy for districts, cities and municipalities: multifunctional use of space to conserve resources
Space is a central component of the urban circular economy and can contribute to improving the quality of life and climate neutrality of cities through targeted transformation. The flexible repurposing of buildings and open spaces enables resource-efficient urban development by preserving existing structures and adapting them to new requirements. Effective vacancy management and strategic land activation are key instruments for municipalities and cities to promote sustainable growth, use land efficiently, and enable high-quality densification.
The repurposing of buildings and districts has far-reaching impacts that go beyond zoning alone. In addition to energy demand and supply infrastructure, it also influences mobility flows, the demand for transport solutions, and the quality of public and semi-public spaces. Aspects such as thermal comfort in open spaces and the quality of stay play a central role in the long-term attractiveness of urban areas.
We support cities, municipalities, and project developers in making the impacts of various planning options visible and in jointly developing viable concepts. Our scientifically grounded analyses make it possible to design sustainable and livable spaces that align long-term urban planning goals with ecological and economic requirements. In doing so, we place particular emphasis on presenting and evaluating both spatial quality and economic effects in a transparent and comprehensible way.