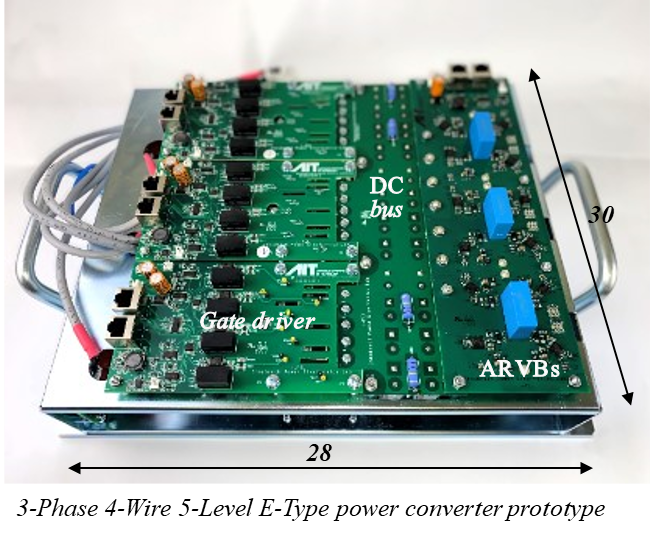
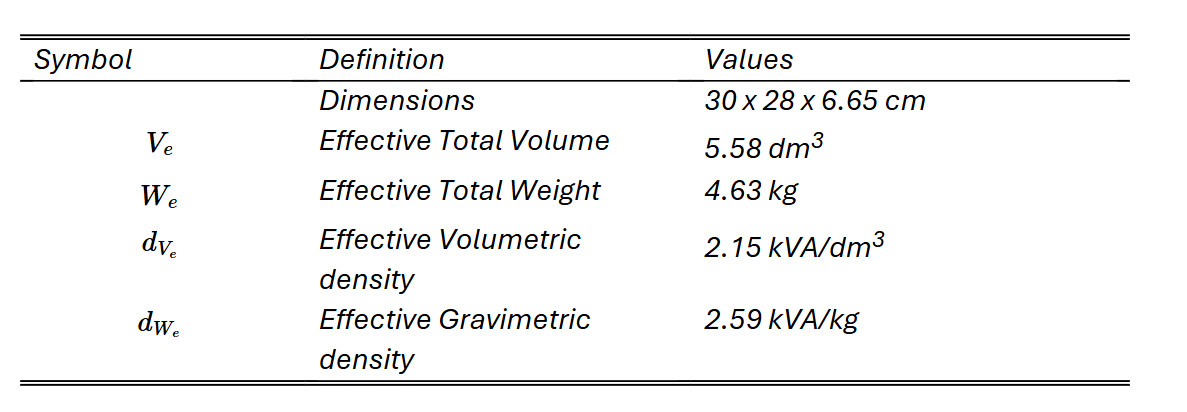
ACHIEVING ULTRA HIGHLY Efficient and compact Power Conversion
One of the key research objectives for emerging power conversion applications is to achieve higher conversion efficiencies while reducing the volume, size and weight of power converters.
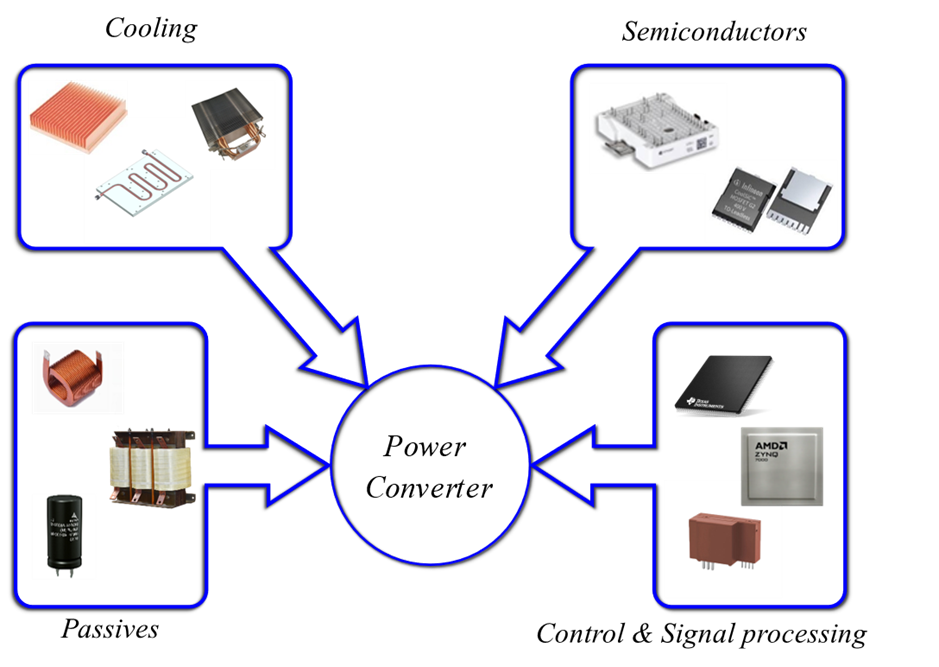
The Role of Multi-level power conversion
Multi-level power conversion essentially uses “more” semiconductors for topologies and “less” passive components.
Semiconductors are mostly made of abundant and lighter materials such as silica or sand, while passives and cooling parts are mostly made of precious and heavier materials such as cooper, aluminum, and steel.
Having smaller and lighter components results in increased volumetric and gravimetric power density.
On the other hand, multi-level topologies are more efficient, so less cooling is required, which also results in a more compact and lighter solution.
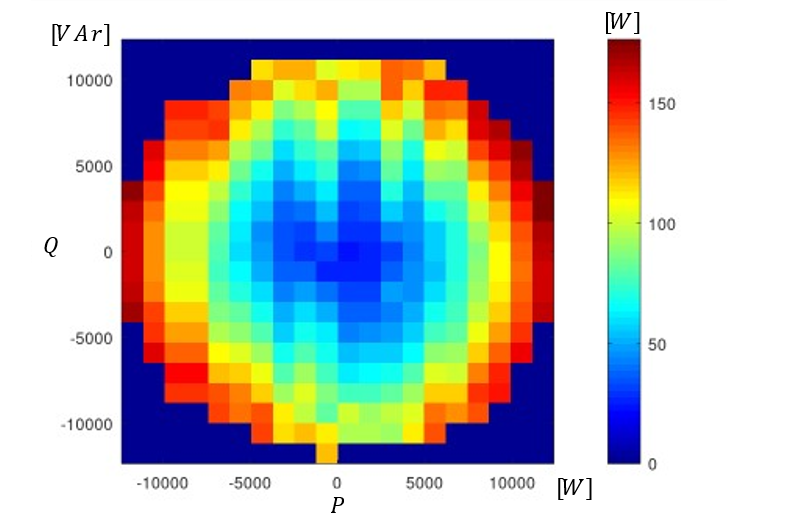
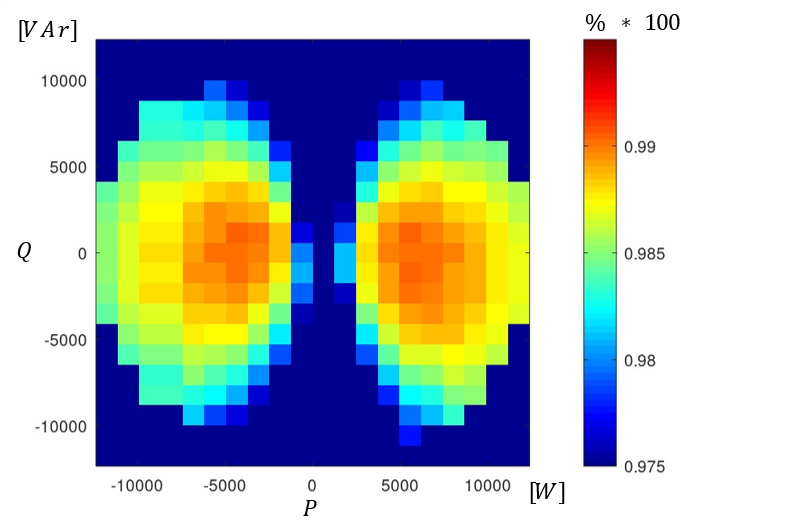
3-Phase 4-Wire 5-Level E-Type power converter PQ diagram: Losses
3-Phase 4-Wire 5-Level E-Type power converter PQ diagram: Efficiency