Future of power Sic & Gan in advanced power electronics
In power electronics, the continuous drive for higher efficiency and increased power density remains a primary objective. However, the still limited operating voltages of GaN devices, due to its physical design characteristics, presents a significant challenge to achieving these goals as standalone semiconductors for operating voltages above 600 V. To address this issue, AIT’s expert team has developed an innovative solution through the hybridization of GaN and SiC technologies. This approach combines the strengths of both semiconductor types, enabling us to maximize efficiency while maintaining high power density, thereby laying the foundation for the next generation of high-performance, reliable systems.
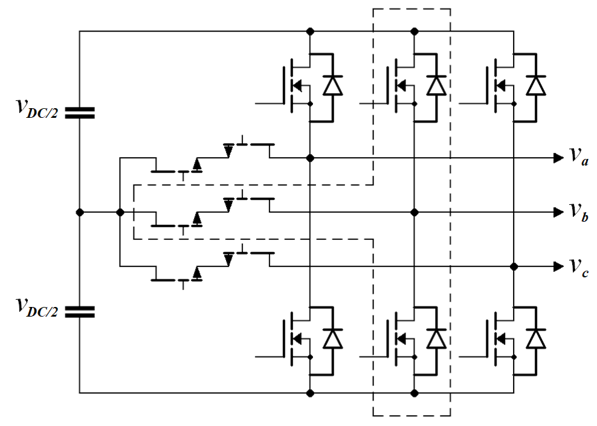
This converter presents the initial development of a novel hybrid T-type converter combining GaN transistors and SiC MOSFETs in one power electronics system.
Why sic- gan- hybridization?
The established method for assessing switching characteristics and examining the dynamic performance of Si, SiC, GaN MOSFETs and IGBTs is the double pulse test (DPT). Double pulse testing allows the precise measurement of energy losses during both the turn-on and turn-off transitions of a device, as well as the assessment of reverse recovery characteristics.
Since GaN devices do not have a body diode, the aim was to find out to what extent the SiC-GaN or GaN-SiC switching losses can be positively influenced. The results indicate that the reverse recovery behavior of the SiC body diode can influence the switching losses of the GaN device. Furthermore, implementing an optimized PCB layout is essential to minimize the parasitic line inductance, which in turn helps to suppress current ringing during the turn-on transition.
T-Type Schema
| Specifications | Application |
| 430 VDC; 15 kWnom; 20 kWpeak; ηsw > 99,2% | Motor Drive, PV Inverter |