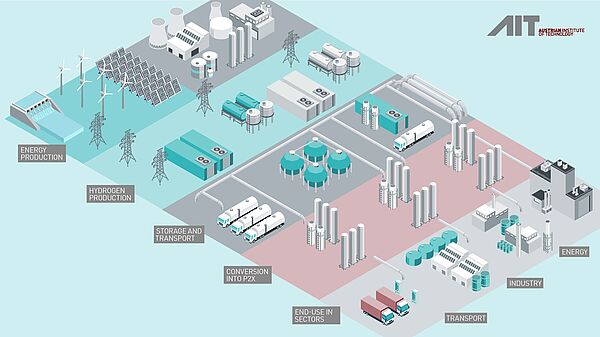
Production of green hydrogen
Green hydrogen is produced by electrolyzing water using electricity from renewable energy sources such as wind power, solar energy or hydropower. In the process, water is split into its components hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen produced in this process is considered “green” because no CO₂ emissions are generated during its production.
Electrolysis process: Alkaline vs. PEM
Electrolysis can be carried out using various technologies, including the alkaline electrolysis process and proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysis. Both technologies have specific advantages:
- Alkaline electrolysis: more mature technology, more cost-effective for large plants.
- PEM electrolysis: Offers faster reaction times and is more flexible in relation to variable energy sources such as wind and solar.
Storing and transporting green hydrogen
Once hydrogen has been produced, it has to be stored and transported. As hydrogen is the smallest and lightest element, storing it poses a technical challenge.
Storage technologies
There are several ways to store hydrogen:
- Pressurized storage: hydrogen is stored at high pressure (200-700 bar) in tanks.
- Liquid storage: Hydrogen is liquefied by cooling it to -253 °C. This reduces the volume, but requires energy-intensive cooling.
- Solid storage: Hydrogen can be stored in chemical compounds known as hydrides. This technology is still in the development phase.
Transportation of hydrogen
Hydrogen can be transported either in compressed form or as liquid hydrogen. Research is also being carried out into converting hydrogen into ammonia or methanol to make transportation more efficient. Pipelines also offer a way of transporting hydrogen over longer distances, but require extensive infrastructure investment.
Conversion and utilization of green hydrogen
Green hydrogen can be used in various sectors to replace fossil fuels and reduce CO₂ emissions.
Utilization in the industry
- Steel production: In the steel industry, hydrogen can be used instead of coke to reduce iron ore, which drastically reduces CO₂ emissions.
- Chemical industry: Hydrogen is an important raw material in the chemical industry, particularly in the production of ammonia and methanol, which in turn are basic materials for many other chemical processes.
Mobility and transportation
- Hydrogen vehicles: Hydrogen-powered fuel cell vehicles (FCEVs) offer an alternative to battery-powered electric vehicles, especially in areas where long ranges or fast refueling times are required, such as heavy goods transport.
- Shipping and aviation: Hydrogen is being researched as a future fuel for ships and aircraft in order to make these sectors, which are difficult to decarbonize, climate-neutral.