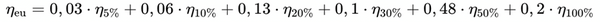INNOVATIVE TESTING TECHNOLOGIES IN THE SMARTEST INVERTER LABORATORY
The inverter laboratory at AIT offers a wide range of testing services based on state-of-the-art technologies. As leading inverter laboratory, it supports companies and developers in testing and optimising components and systems. Here you receive precise and reliable results – whether for electrical tests, lifetime simulations or grid code compliance testing.
What is the Smartest Inverter Laboratory?
The SmartEST inverter laboratory is one of the most modern testing facilities in Europe, specialising in the testing and developing of inverters, energy systems, and smart grid components. The aim is to ensure the reliability and efficiency of these technologies while meeting the requirements of the modern energy grids.
Service offerings of the Smartest Inverter Laboraory
The AIT inverter laboratory offers a wide range of services specifically tailored to the needs of developers and manufacturers. From component tests to the simulation of complex energy systems - the SmartEST inverter laboratory covers all requirements.
Testing of Inverter components and Systems
The laboratory enables testing under realistic conditions, including simulated grids and primary energy sources. Electrical, functional, and performance tests are carried out in accordance with the latest grid codes to ensure compliance with legal requirements.
Simultaneous tests of power and communications Interfaces
The integration of power and communication interfaces is crucial to the interoperability of modern energy systems. The SmartEST inverter laboratorytests these interfaces under real-world conditions to ensure optimal functionality.
OBJECTIVES OF PERFORMANCE TESTS
These tests are designed to:
- evaluate efficiency in order to minimise losses.
- Verify compliance with standards, particularly regarding grid synchronisation and safety functions.
- Ensure reliability and longevity.
- Analyse performance under varying conditions (load changes, voltage fluctuations, and temperatures).
KEY PERFORMANCE TESTS
Efficiency tests
Maximum efficiency:
Evaluation of the maximum achievable efficiency at rated power.
- Example: An Inverter with 97 % efficiency converts 97 % of DC-Power into AC, while 3 % are lost as heat
Partial load efficiency:
Efficiency at different load levels (e.g. 10%, 25%, 50%, 75% of rated power). Inverters often operate below maximum capacity, making partial load efficiency crucial.
European efficiency:
Average efficiency based on typical load profiles in Europe.
PERFORMANCE AND LOAD TESTS
Continuous performance tests:
The inverter is operated at maximum power over an extended period to test thermal stability and load capacity.
Overload capability:
Testing the behaviour under short-term overload conditions (e.g. 110 % or 120% of rated power). This is important for systems operating with varying loads and peak demands.
Voltage and frequency stability:
Verfication whether the inverter operates stable under varying grid conditions (e.g. voltage fluctuations)
Island grid Tests
- Self-consumption in standby mode:
Measurement of power consumption when the inverter is inactive to minimise energy losses in idle mode. - Off grid capability:
Test for island grid applications where the inverter must operate synchronously without a grid connection.
Dynamic tests
- Load change behavior:
Testing the inverter under sudden changes in load or input voltage (e.g. due to varying solar irradiation in PV systems) - Regulating behavior:
How quickly and accurately the inverter responds to changes in input and grid voltage.
Standards and Guidelines for inverter Testing
Inverter tests are guided by international standards as:
- IEC 62109-1/-2: Safety of inverters.
- IEC 61727: Requirements for grid connection.
- VDE-AR-N 4105: German standard for feeding into low-voltage grids.
- IEEE 1547: Requirements for grid synchronisation and islanding prevention.
- IEC 61683: Efficiency measurement of inverters.
SIMULATIONS IN THE SMARTEST INVERTER LABORATORY
Grid simulation
The grid simulation in the inverter laboratory is a crucial component for testing inverters under realistic and controlled conditions. In this process, an artificial power grid is modelled to simulate typical or extreme grid conditions. This allows for verifying the grid compatibility and protective functions of the inverter before it is deployed in a real-world environment.
- 3 independent laboratory grids with variable grid impedances for up to 1000 kVA, flexible neutral point configurations, and grounding systems.
- 2 independent grid simulators with high bandwidth: 0 to 480 V three-phase AC, 800 kVA, and variable frequency range.
- 3-phase symmetric or asymmetric operation
- Facilities for LVRT (Low Voltage Ride-Through).
Simulation and testing of complete systems
With power Hardware-in-the-Loop (P-HIL) experiments and multi-domain co-simulations complete generation systems can be simulated and tested. This technology enables a rapid modelling and prototyping.
ENVIROMENT SIMULATION
In specialised test chambers, devices can be tested under extreme temperature conditions and varying humidity levels. This is ideal for accelerated lifetime testing.
- Temperature tests:
Operation under extreme temperatures (e.g. -40 °C to +120 °C) to verify the cooling mechanisms and efficiency. - Humidity and corrosion tests:
Particularly for outdoor inverters, tests are conducted to to determine whether moisture or corrosive environments (e.g. salt mist in coastal regions) affect functionality.
DC Sources and battery simulation
Dynamic PV array simulators
The laboratory is equipped with six independent simulators, providing 1500 V and 1100 kW, capable of replicating realistic conditions for solar systems.
Bidirectional DC sources
These enable the emulation of battery systems to test their performance and reliability
PRECISE Data ACQUISITION and analysis
High-precision power analysers and advanced data acquisition systems enable the simultaneous recording of multiple data streams, providing detailed insights into the tested systems.
The SmartEST laboratory at AIT is the ideal destination for manufacturers, developers, and researchers who rely on reliable testing and innovative solutions. With state-of-the-art technology and comprehensive services, the laboratory supports the energy transition and advances the technologies of the future.
FAQs
- Which types of tests does the SmartEST laboratory offer?
The laboratory offers electric, functional, performance and lifetime tests as well as simulations of smart grid scenarios. - Which systems can be tested?
From decentralised generators and battery systems to complete energy plants, the range of services is comprehensive. - Which temperatures can be simulated in the test chambers?
The temperature ranges from -40 °C to +120 °C, with humidity levels between 10% and 98%; combined testing may be subject to certain limitations. - How are the tests accredited?
The tests are either directly accredited or conducted using a witness procedure within an accredited scope - What is the maximum size of devices that can be tested?
Devices with dimensions of up to 3.60 x 2.60 x 2.80 m can be tested. - What is the maximum weight of the test specimen?
This depends on the installation location—10 tonnes outside the test chamber and 3 tonnes inside the test chamber.