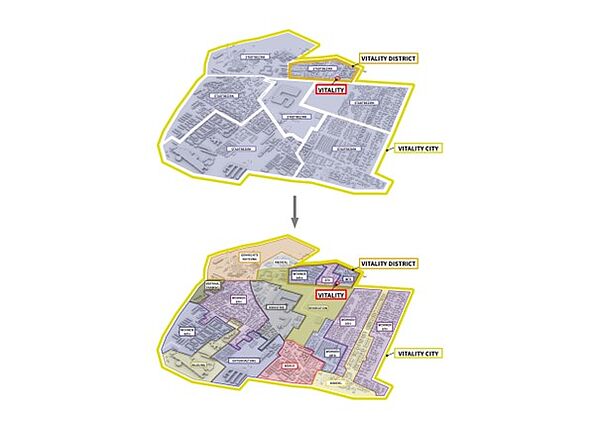
The VITALITY District project builds on the results of the VITALITY project, which developed an assessment tool for the early planning phase of photovoltaic systems for large buildings.
Energy storage systems in districts offer various electrical and thermal storage options (e.g., seasonal underground storage, thermal component activation, water storage). They help buffer peak loads and surpluses, optimizing energy efficiency within the district. To achieve this, buildings, storage systems, and the district must be connected to and interact with the power grid.
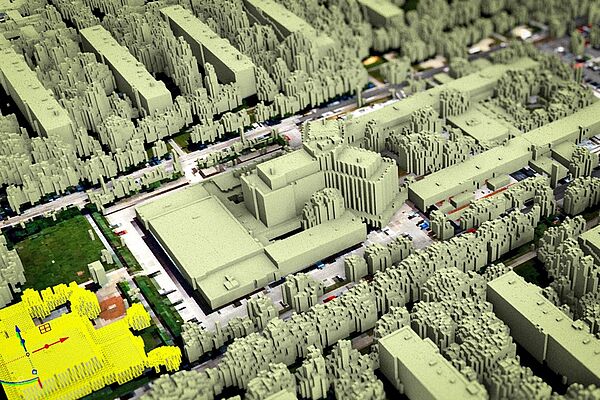
The VITALITY CITY project expands this approach to entire cities. Through dynamic overall energy balancing, existing and newly planned urban areas can be analyzed in the city's energy context. Automated 3D mapping data enables rapid energy demand assessment, while solar potential is directly integrated into the balance. Algorithms calculate CO₂ emissions and support both ecological and economic evaluations of the urban area. The goal is an objective, efficient, and fast energy analysis to identify targeted measures for climate neutrality. The calculation tool combines existing methods and fills gaps to provide a comprehensive urban energy assessment.
Project goals
The VITALITY District project builds on the results of the VITALITY project, which developed an assessment tool for the early planning phase of photovoltaic systems for large buildings.
Energy storage systems in districts offer various electrical and thermal storage options (e.g., seasonal underground storage, thermal component activation, water storage). They help buffer peak loads and surpluses, optimizing energy efficiency within the district. To achieve this, buildings, storage systems, and the district must be connected to and interact with the power grid.
The VITALITY CITY project expands this approach to entire cities. Through dynamic overall energy balancing, existing and newly planned urban areas can be analyzed in the city's energy context. Automated 3D mapping data enables rapid energy demand assessment, while solar potential is directly integrated into the balance. Algorithms calculate CO₂ emissions and support both ecological and economic evaluations of the urban area. The goal is an objective, efficient, and fast energy analysis to identify targeted measures for climate neutrality. The calculation tool combines existing methods and fills gaps to provide a comprehensive urban energy assessment.
Role of AIT
AIT focuses on highly specialized topics such as capturing existing buildings from publicly available geospatial data and visualizing (CIL) the results of dynamic calculations. This ensures user-friendly operability.
![[Translate to English:] Smart and Carbon-Neutral Urban Development Symbolfoto: Das AIT ist Österreichs größte außeruniversitäre Forschungseinrichtung](/fileadmin/_processed_/a/d/csm_Thermalkataster_Hotspots_7969d57e54.jpg)