Wind power provides around 11% of Austria's electricity. This makes it the country's second most important sustainable energy source after hydropower. However, due to the alpine characteristics of the Austrian climate, significant icing of the rotor blades occurs at many current and future potential sites for wind turbines. Wind energy is a particularly suitable alternative energy source in winter, when less energy can be expected from photovoltaics and hydropower. However, icing can significantly reduce the reliability and yield of wind turbines in winter.
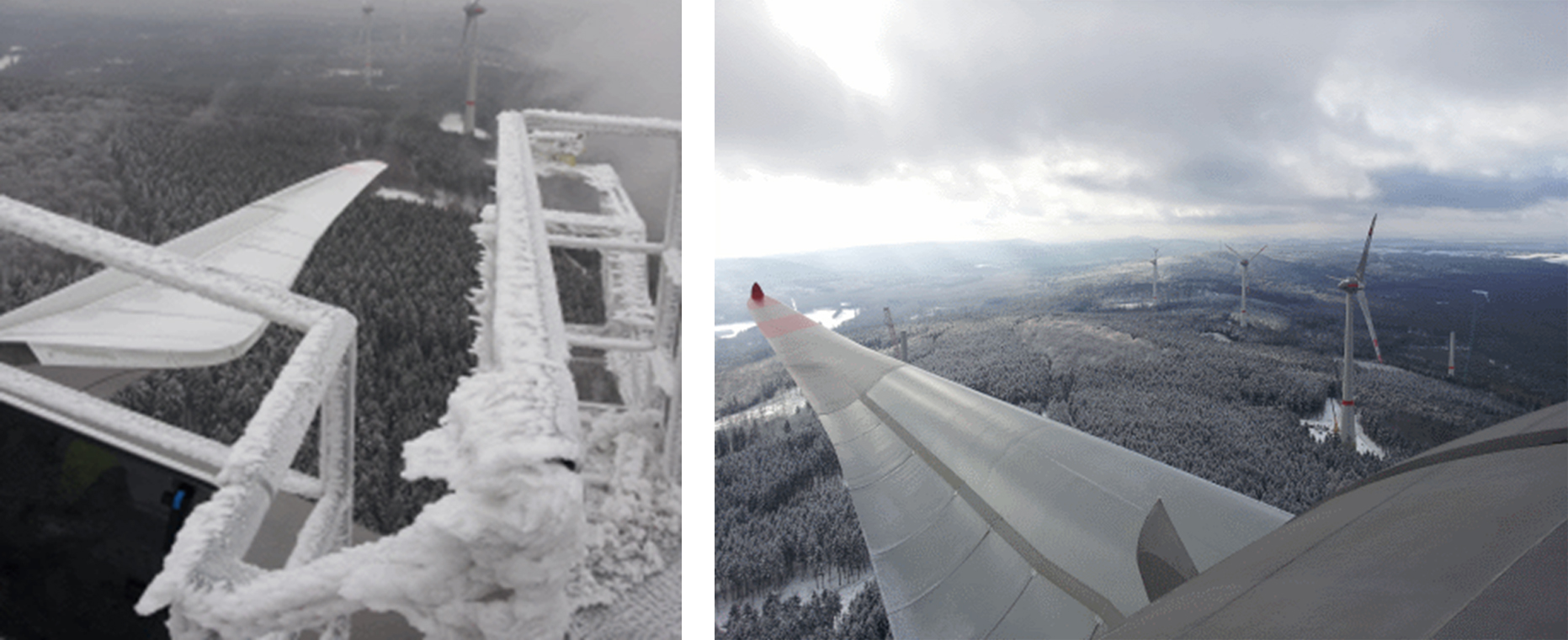
Icy wind turbines, as shown in the picture on the left, cause high costs. ©VERBUND
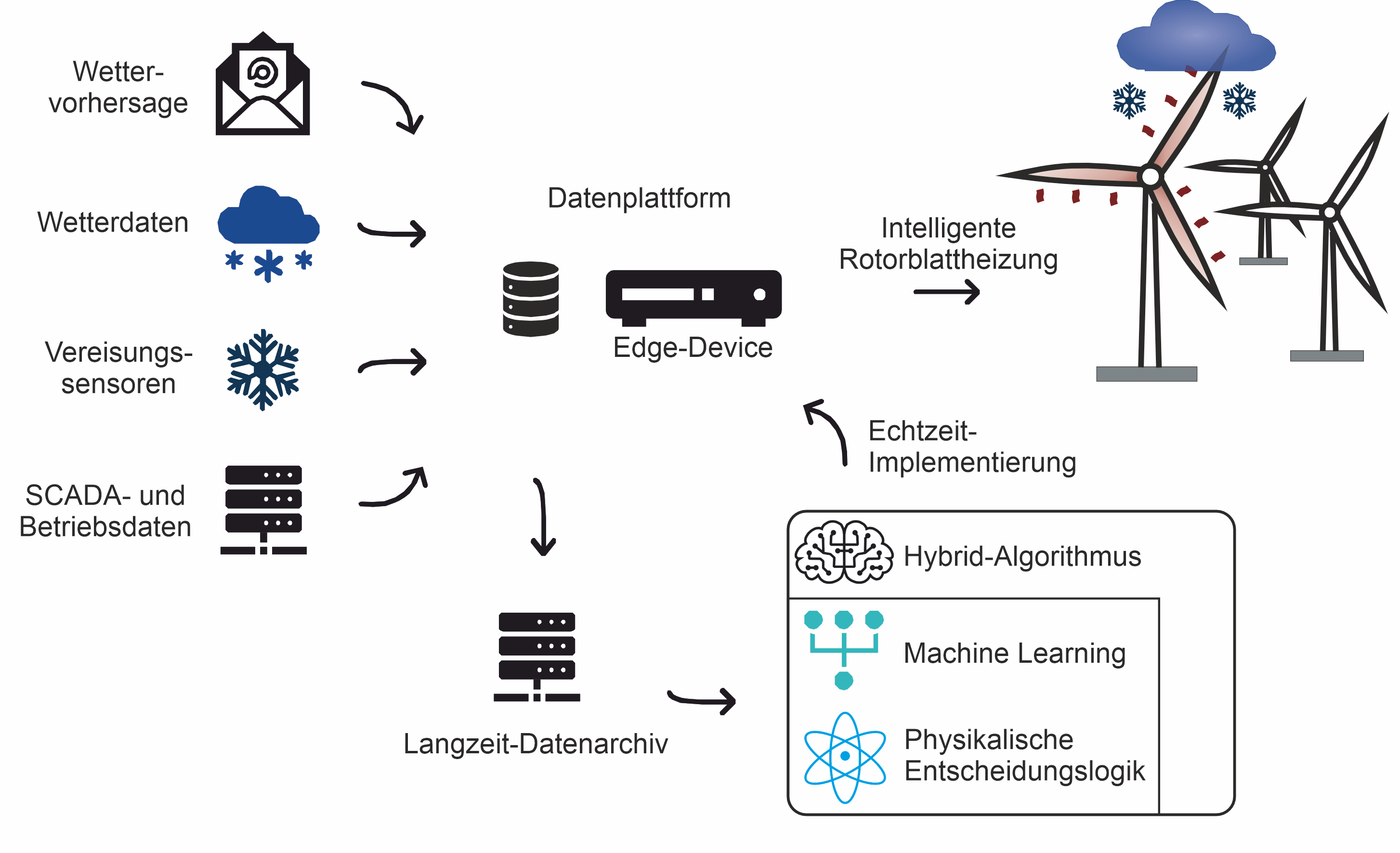
To minimise future production losses caused by icing in wind turbines, the SOWINDIC project investigated an intelligent heating algorithm for wind turbine rotor blades, based on real-time and forecast data. The central components of this are:
- A data archive for the long-term storage and provision of collected data.
- A real-time capable data platform/edge device as a runtime environment for the SOWINDIC algorithms that activate the rotor blade heating of a wind turbine.
- Research turbines with operating permits, options for intervention in rotor blade heating control, and additional sensors for recording background information.
- Real-time executable algorithms for the intelligent control of rotor blade heating.
Project idea and components of the project
Smart rotor blade heating
As part of the SOWINDIC research project, a real-time data platform was developed to optimise the control of wind turbine rotor blade heating. Multiple models are run in parallel on an edge device, with the option to select which model controls the rotor blade heating on a modular basis. These models comprise both physically motivated decision logic and various neural networks, which control the optimised rotor blade heating and provide interpretable intermediate results. These two approaches were also combined into a hybrid model to further enhance the performance of the intelligent rotor blade heating system.
Project partner
Meteotest AG
Universität Wien, Data Science @ Uni Vienna
Verbund Green Power GmbH
Funding
The project SOWINDIC (Smart operation of wind turbines under icing conditions) has received funding from Bundesministerium für Klimaschutz, Umwelt, Energie, Mobilität, Innovation und Technologie (BMK) within the program „Energieforschung“. Project number 885057
Links
energieforschung.at/projekt/smart-operation-of-wind-turbines-under-icing-conditions-2/
https://projekte.ffg.at/projekt/4032457
Publications
- Fritze G., Gruber D., Gerber F., Froidevaux P., Gruber M., Kloiber S., Sedlmayer M., Bot R.: „Data Management and Real-time Algorithm Deployment for Advancing Anti-Icing Rotor Blade Heating In Wind Turbines“, International Wind Energy Conference Winterwind (2024).
- IGW Wind Industry Stakeholder Meeting: “A Smart Algorithm for Wind Turbine Controlling
- IEA (International Energy Agency) Wind Task54 on Wind Energy in Cold Climate, insbesondere im Subtask “Blade Heating Envelope”, inklusive Workshop bei der Winterwind 2023, Åre, 27.3.2023 und Winterwind 2024, Åre, 18.3.2024
- Gerber, F., Froidevaux, P., Sedlmayer, M., Bot, R., Gruber, D., Glück, T., Burchhart, T., Kloiber, S.: “A smart algorithm for wind turbine controlling under icing conditions”, International Wind Energy Conference Winterwind (2022).
- Gerber, F., Froidevaux, P., Sedlmayer, M., Bot, R., Gruber, D., Fritze, G., Glück, T., Burchhart, T., Kloiber, S.: “A smart algorithm for wind turbine controlling under icing conditions”, IGW Wind Industry Stakeholder Meeting, Wien (2022).
- Gerber, F., Froidevaux, P.: “Can we make better use of ice protection systems?”, International Wind Energy Conference Winterwind (2023).
- Gerber, F., Froidevaux, P., Sedlmayer, M., Bot, R., Gruber, M., Kloiber, S., Gruber, D., Fritze, G.: “Smart control for blade heating systems – physics or machine learning?”, International Wind Energy Conference Winterwind (2024).
- Kooperation mit dem Projekt SOPWICO, welches durch VGBE finanziert wird, bei Entwicklung des Algorithmus sowie geplante Anwendung und Verfeinerung des Algorithmus für drei weitere Windparks.
- FGP‘22 – French German Portuguese Conference on Optimization 2022: „A Relaxed Inertial Forward-Backward-Forward Algorithm for Solving Monotone Inclusions with Application to GANs“; Porto, Portugal, 05.05.2022; basierend auf Bot et al. 2023a.
- 15th Viennese Conference on Optimal Control and Dynamic Games: „Two (Forward) Steps at a Time – Training GANs with Tseng’s Method“; Wien, 14.07.2022; basierend auf Böhm et al. 2022.
- ICCOPT 2022 – International Conference on Continuous Optimization 2022: „An Accelerated Minimax Algorithm for Convex-concave Saddle Point Problems with Nonsmooth Coupling Function“; Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, USA, 27.07.2022; basierend auf Bot et al. 2023b.
- ICML 2023 - 40th International Conference on Machine Learning: “A Fast Optimistic Method for Monotone Variational Inequalities”, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, 23.07.2023; basierend auf Sedlmayer et al. 2023.
- The OR Society Annual Conference 2023 (OR 65): “A Fast Optimistic Method for Monotone Variational Inequalities”, Bath, UK, 13.09.2023; basierend auf Sedlmayer et al. 2023.
- Winterwind 2023: “Challenges for a smart algorithm controlling wind turbines under icing conditions”, Åre, 29.3.2023 (VERBUND).
- VGB Webinar "Operation of Wind Power Plants in Cold Climate 2021“ (27.10.2021 – 28.10.2021).
- Böhm, A., Sedlmayer, M., Csetnek, E.R., and Bot, R.I.: "Two steps at a time--taking GAN training in stride with Tseng's method." SIAM Journal on Mathematics of Data Science 4 (2), 750-771, 2022.
- Bot, R.I., Sedlmayer, M., and Vuong, P.T.: “https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=de&user=696L6cEAAAAJ&citation_for_view=696L6cEAAAAJ:u-x6o8ySG0sC.” Journal of Machine Learning Research 24 (8), 1-37, 2023a.
- Bot, R.I., Csetnek, E.R., and Sedlmayer, M.: "An accelerated minimax algorithm for convex-concave saddle point problems with nonsmooth coupling function." Computational Optimization and Applications 86 (3), 925-966, 2023b.
- Sedlmayer, M., Nguyen, D.K., and Bot, R.I.: “A Fast Optimistic Method for Monotone Variational Inequalities.“ Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR 202:30406-30438, 2023.
Supported by
APG Austrian Power Grid AG (https://www.apg.at/)
EVN Energieversorgung Niederösterreich AG (https://www.evn.at/)
eologix sensor technology GmbH (https://www.eologix-ping.com/)
Universität Bremen (https://www.uni-bremen.de/)
KELAG-Kärntner Elektrizitäts AG (https://www.kelag.at/)
Windkraft Simonsfeld AG (https://www.wksimonsfeld.at/)
Energie Steiermark AG (https://www.e-steiermark.com/)
ImWind Erneuerbare Energie GmbH (https://www.imwind.at/)
Burgenland Energie AG (https://www.burgenlandenergie.at/)
Österreichische Bundesforste AG (https://www.bundesforste.at/)
vgbe energy e.V. (https://www.vgbe.energy/)
Austro Control Digital Services GmbH (https://www.austrocontrol.at/)